A ISO document has a number rules that are essential for understanding. It is important that abbreviations are clear and precise. Certain forms of punctuation should be avoided. These include symbols for quantities or forms of language. These guidelines are intended to make it easier for the reader to comprehend the ISO document and its contents.
Formulas
Implementing electronic ISO document forms can boost your company's quality processes, regulatory compliance, and customer satisfaction. Remember to keep these forms simple, break them down into data types, and ensure they are part or a larger process. Agile development is crucial. User requirements are important. User testing can be very useful, as it can show you issues that were not obvious. It is also important to provide training for all software-specific users.

Symbols for quantities
The symbols used to represent quantities in ISO documents are abbreviated terms. These symbols, which are often abbreviated terms and written in italics instead of numbers or words written in lowercase, are used to represent quantities in ISO documents. Some abbreviations have special meanings like 'net present value' and 'internal return on investment'. The standard also specifies the types of symbols that should be used for quantities.
Acronyms
You've probably come across some common acronyms if you read ISO documents often. The first acronym is CAR (Corrective Action Request). The Corrective Action Request (CA) is an activity that initiates a Corrective Activity. This usually involves investigating a problem, identifying the root cause and preventing it from recurring. It can also refer to the whole Corrective Action Lifecycle.
Language
Language of ISO document is vital in making sure that the intended audience understands the document. There are certain conventions that characterize this language. It is common to use abbreviations, but the first words of a term must be capitalized. For radio frequency, however, it is not acceptable to use the abbreviation d.c.
Formatting
Documentation is an essential aspect of ISO standards. Some organizations overdocument, making it difficult to maintain a flexible system. This problem can be avoided by ensuring that your documentation is in the right structure and style.

Publishing
ISO publishes documents in different formats. ISO documents can be called IEC standards, or ISO standards. These documents are the result of an ISO/IEC JTC 1 committee and the American Society for Testing and Materials. ISO standards can differ from ASTM standards. Some standards do not have all the details and are not published. Their designations are often not included in the titles of published works.
FAQ
How can a manager motivate his/her staff?
Motivation can be defined as the desire to achieve success.
Enjoyable activities can motivate you.
Another way to get motivated is to see yourself as a contributor to the success of the company.
You might find it more rewarding to treat patients than to study medical books if you plan to become a doctor.
Another type of motivation comes from within.
You may feel strongly that you are responsible to help others.
Maybe you like working hard.
Ask yourself why you feel so motivated.
Next, think of ways you can improve your motivation.
What's the difference between Six Sigma and TQM?
The main difference between these two quality management tools is that six sigma focuses on eliminating defects while total quality management (TQM) focuses on improving processes and reducing costs.
Six Sigma is a method for continuous improvement. This approach emphasizes eliminating defects through statistical methods like control charts, Pareto analysis, and p-charts.
This method attempts to reduce variations in product output. This is done by identifying and correcting the root causes of problems.
Total quality management is the measurement and monitoring of all aspects within an organization. This includes training employees to improve their performance.
It is frequently used as an approach to increasing productivity.
What is the difference of a program and project?
A project is temporary while a programme is permanent.
A project has usually a specified goal and a time limit.
It is often carried out by a team of people who report back to someone else.
A program will usually have a set number of goals and objectives.
It is often done by one person.
Statistics
- This field is expected to grow about 7% by 2028, a bit faster than the national average for job growth. (wgu.edu)
- The BLS says that financial services jobs like banking are expected to grow 4% by 2030, about as fast as the national average. (wgu.edu)
- 100% of the courses are offered online, and no campus visits are required — a big time-saver for you. (online.uc.edu)
- The average salary for financial advisors in 2021 is around $60,000 per year, with the top 10% of the profession making more than $111,000 per year. (wgu.edu)
- As of 2020, personal bankers or tellers make an average of $32,620 per year, according to the BLS. (wgu.edu)
External Links
How To
How do you implement Quality Management Plans (QMPs)?
Quality Management Plan (QMP), which was introduced in ISO 9001:2008, provides a systematic approach to improving processes, products, and services through continual improvement. It emphasizes on how to continuously measure, analyze, control, and improve processes, product/service, and customer satisfaction.
QMP is a standard way to improve business performance. QMP helps improve production, service delivery and customer relationships. QMPs should address all three dimensions: Products, Services, and processes. The QMP that only addresses one aspect of the process is called a Process QMP. If the QMP is focused on a product/service, it's called a QMP. And when the QMP concentrates on Customer Relationships, it is called "Customer" QMP.
There are two key elements to implementing a QMP: Strategy and Scope. These are the following:
Scope: This describes the scope and duration for the QMP. For example, if your organization wants to implement a QMP for six months, this scope will define the activities performed during the first six months.
Strategy: This is the description of the steps taken to achieve goals.
A typical QMP consists of 5 phases: Planning, Design, Development, Implementation, and Maintenance. Below is a description of each phase:
Planning: In this stage the QMP's objectives and priorities are established. In order to fully understand and meet the needs of all stakeholders involved in this project, they are consulted. Next, you will need to identify the objectives and priorities. The strategy for achieving them is developed.
Design: During this stage, the design team develops the vision, mission, strategies, and tactics required for the successful implementation of the QMP. These strategies are implemented by the development of detailed plans and procedures.
Development: This is where the development team works to build the capabilities and resources necessary for the successful implementation of the QMP.
Implementation is the actual implementation of QMP according to the plans.
Maintenance: This is an ongoing procedure to keep the QMP in good condition over time.
Several additional items should be added to the QMP.
Participation by Stakeholders is essential for the QMP's continued success. They need to be actively involved in the planning, design, development, implementation, and maintenance stages of the QMP.
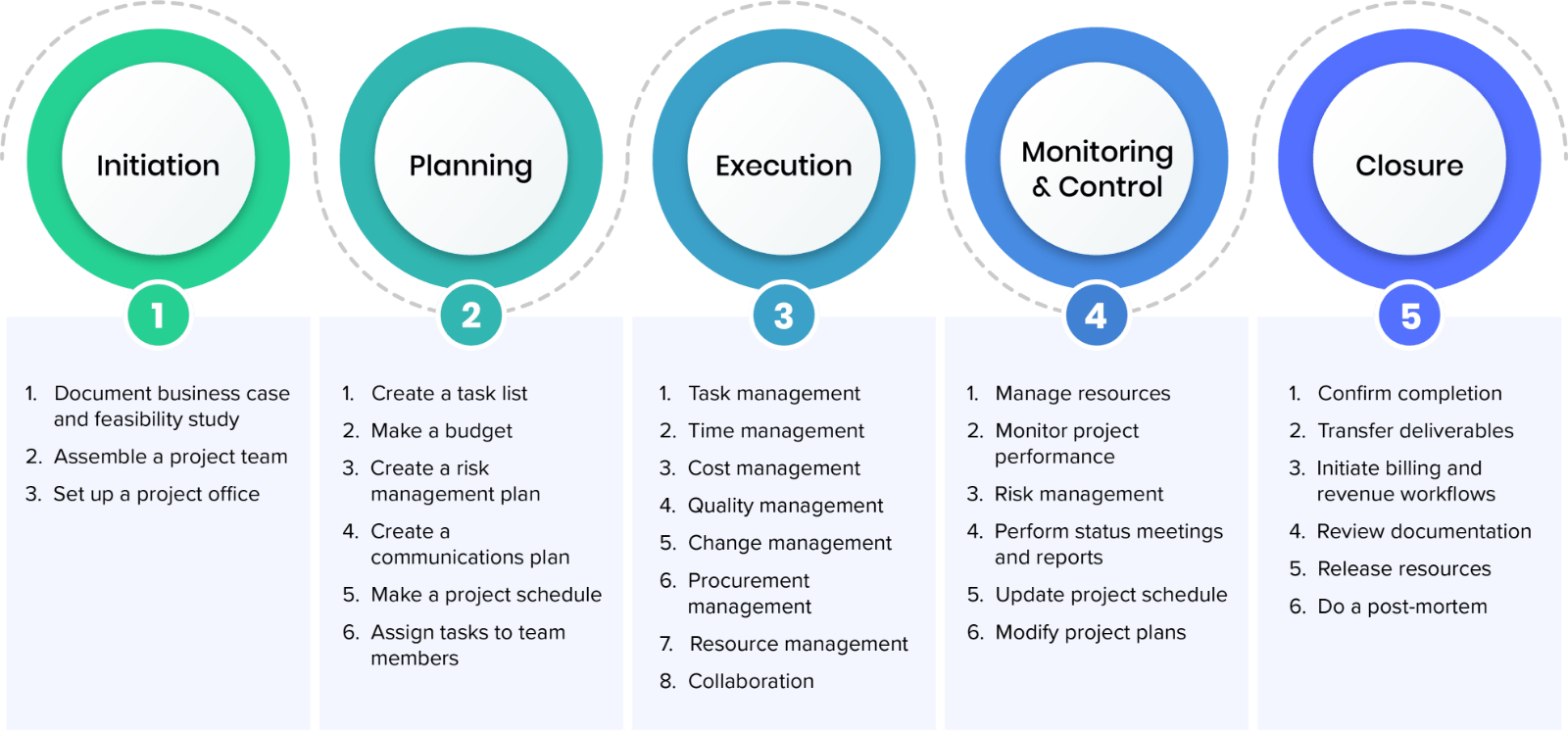
Project Initiation - A clear understanding of the problem statement, and the solution is necessary for any project to be initiated. This means that the initiator should know why they want something done and what they hope for from the end result.
Time frame: The QMP's timeframe is critical. A simple version is fine if you only plan to use the QMP for a brief period. For a long-term commitment you may need more complicated versions.
Cost Estimation is another important aspect of the QMP. Without knowing how much you will spend, planning is impossible. Before you start the QMP, it is important to estimate your costs.
The most important thing about a QMP is that it is not just a document but also a living document. It evolves as the company grows and changes. It should be reviewed regularly to ensure that it meets current needs.